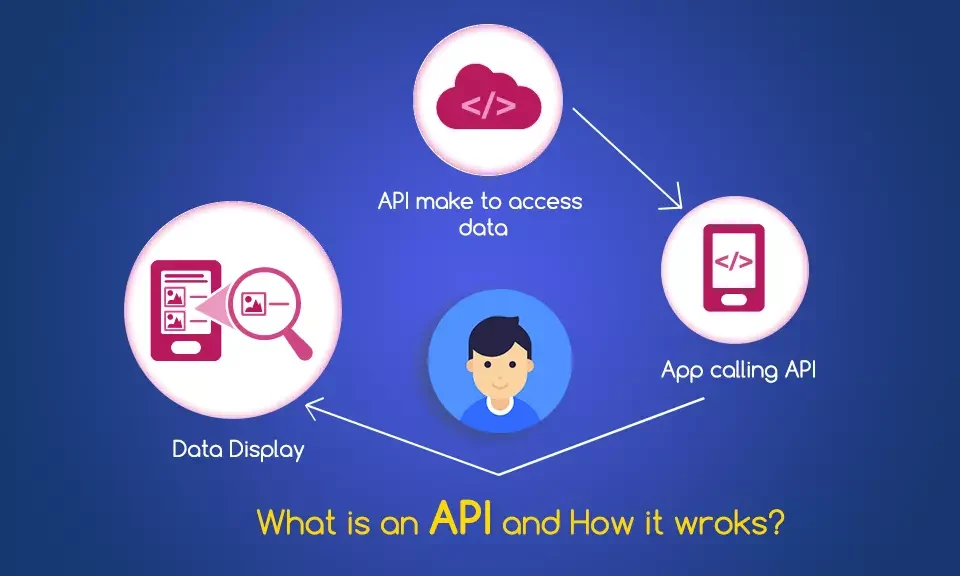
What is an API? Real-World Examples for Beginners
August 5, 2025
AI and Entrepreneurship: Opportunities And Challenges
August 5, 2025Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming industries — from healthcare and finance to transportation and education. However, as AI systems become more powerful, questions about ethics, safety, and accountability have grown louder. This is where regulation in shaping AI’s future becomes vital. Regulations act as guiding frameworks, ensuring AI is developed and deployed responsibly, balancing innovation with public trust.
(Learn more about AI ethics at European Commission AI Regulation.)
Why Does Regulation Matter in AI?
AI’s rapid growth brings opportunities but also significant risks — bias in algorithms, privacy violations, job displacement, and even misuse in warfare. Without regulatory frameworks, companies might prioritize speed and profit over ethics and safety.
Regulation in shaping AI development ensures:
- Ethical AI practices (transparency, fairness, accountability)
- Consumer protection (preventing data misuse and discrimination)
- Global trust (encouraging adoption of AI technologies)
- Sustainable innovation (balancing progress with safeguards)
(See OECD AI Principles for international guidelines.)
Synonyms for “Regulation in Shaping”
To avoid overusing the main keyword, here are natural variations used throughout this article:
- Governance guiding AI
- Oversight in AI development
- Legal frameworks for AI
- AI policy direction
- Rules influencing AI adoption
- Ethical frameworks shaping AI
Current Global AI Regulations
European Union (EU)
The EU’s AI Act is one of the world’s first comprehensive AI laws. It categorizes AI systems by risk (minimal to unacceptable) and imposes strict requirements on high-risk applications like biometric surveillance.
(More at EU AI Act Overview.)
United States
While the U.S. lacks a unified AI law, frameworks like the AI Bill of Rights provide guidelines on transparency, privacy, and discrimination prevention. Agencies like the FTC are increasingly monitoring AI usage in businesses.
(Details: White House AI Bill of Rights.)
China
China has implemented strict rules on algorithms, focusing on content moderation, deepfakes, and recommendation systems to maintain social stability and prevent misinformation.
India
India currently promotes a light-touch regulatory approach to encourage AI innovation but is working toward an AI ethics policy framework.
(Check NITI Aayog AI Strategy.)
Benefits of AI Regulation
- Promotes Responsible Innovation
Rules ensure developers prioritize ethics without stifling creativity. - Builds Public Trust
Transparent frameworks reassure users about AI safety and fairness. - Encourages Global Collaboration
Harmonized regulations help companies operate across borders. - Mitigates Risks
Prevents harmful consequences like biased algorithms or data breaches.
Challenges in Regulating AI
- Rapid Technological Change: Laws often lag behind evolving AI capabilities.
- Global Consistency: Different countries have varying priorities, creating fragmented policies.
- Balancing Innovation and Control: Overregulation can slow progress; under-regulation can lead to misuse.
- Enforcement Difficulties: Monitoring AI systems and ensuring compliance is complex.
(See Stanford HAI Policy Research for in-depth challenges.)
The Future of AI Governance
The future of regulation in shaping AI will likely involve:
- International agreements (similar to climate accords) to align global standards.
- Dynamic policies that evolve with technology advancements.
- Public-private partnerships to co-create fair and enforceable AI rules.
- AI Ethics Boards within corporations for internal oversight.
(Explore World Economic Forum AI Governance.)
Real-World Examples
- Healthcare AI: Regulations ensure diagnostic tools are accurate and approved by health authorities before public use.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Safety laws mandate testing and fail-safes to prevent accidents.
- Finance: AI-driven credit scoring must comply with anti-discrimination laws to ensure fairness.
(Learn about Responsible AI in Healthcare.)
FAQs on AI Regulation
1. Why do we need AI regulation?
To ensure ethical, safe, and unbiased AI systems that serve society responsibly.
2. Will regulation slow AI innovation?
Proper regulation guides innovation rather than halting it, ensuring long-term trust and adoption.
3. Who regulates AI globally?
No single body; multiple governments and organizations (EU, OECD, UN) collaborate to set standards.
4. What happens if AI is unregulated?
Potential harms include biased algorithms, privacy breaches, and unsafe autonomous systems.
Conclusion
The role of regulation in shaping the future of AI cannot be overstated. As AI becomes deeply embedded in daily life, legal and ethical frameworks are crucial to protect individuals, foster innovation, and create trust in technology. Collaborative global efforts will define how AI evolves — responsibly and for the benefit of all.
(For more AI insights, explore Chatrashala AI Blogs or take Coursera’s AI Ethics Course.)