DBMS vs. RDBMS: Key Differences Explained Simply
August 4, 2025
Role of Regulation in Shaping the Future of AI
August 5, 2025In today’s connected world, software applications rarely work in isolation. They interact and share data seamlessly — all thanks to APIs (Application Programming Interfaces). But API introduction, and why is it so important for modern development?
In simple terms, an API is like a bridge that allows two different applications to communicate. From logging in with Google to embedding maps or paying via PayPal, APIs power everyday features you use online.
(Want to explore more about modern tech? Check Chatrashala Tech Blogs for detailed beginner guides.)
Understanding the Basics: What is an API?
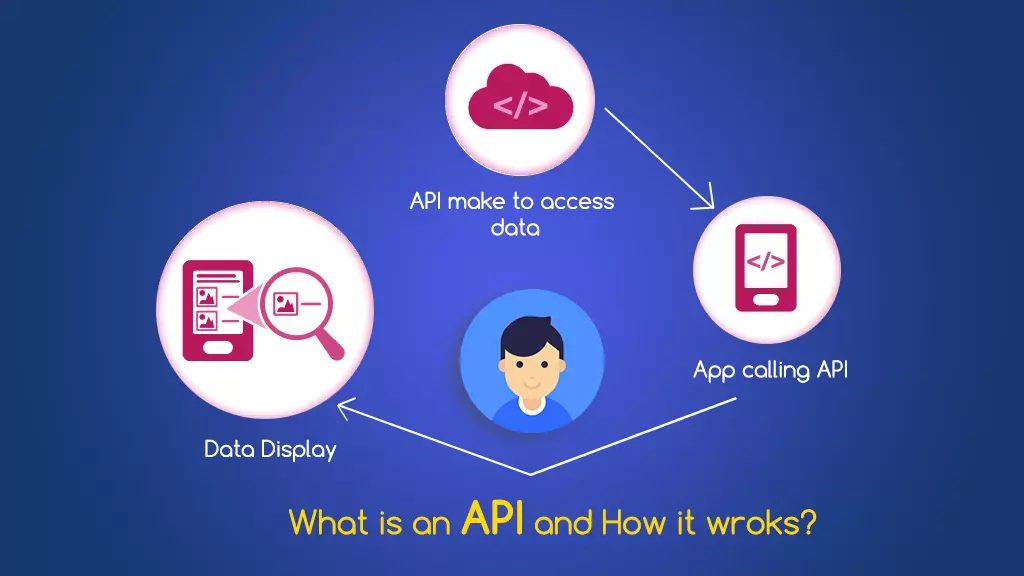
An API is a set of rules and protocols that allow software programs to exchange data. It defines how applications request and send information to each other.
Think of it like a restaurant waiter: you (the client) ask for food (data) via the waiter (API), who delivers it from the kitchen (server).
Synonyms and related phrases: API meaning, API explained, application programming interface, API examples.
(For technical definitions, see Red Hat API Overview.)
How Does an Understanding API Work?
APIs function through requests and responses:
- A client sends a request to the API endpoint.
- The API processes the request and retrieves the required data.
- The response is sent back to the client application.
Example: A weather app doesn’t gather data itself. It requests weather data from a service like OpenWeatherMap API, which sends the information back to display on your screen.
Why Are APIs Important?
APIs are essential because they:
- Enable smooth integration between services (e.g., payment gateways, social logins).
- Save time and resources by reusing existing solutions instead of building from scratch.
- Enhance user experience by connecting multiple services (maps, payments, notifications).
- Support innovation — new apps can leverage existing platforms to create value.
(Read more benefits at IBM API Guide.)
Types of APIs
1. Web APIs
Used to connect web servers and clients; includes REST and SOAP APIs.
2. Open (Public) APIs
Accessible by external developers, like Twitter API or Google Maps API.
3. Internal (Private) APIs
Restricted to internal use within an organization for internal services.
4. Partner APIs
Shared between business partners to enable controlled integrations (e.g., airline and travel sites).
5. Hardware APIs
Allow software to interact with hardware devices (e.g., smartphone camera API).
(See Microsoft API Design Guide for best practices.)
Real-World API Examples
Google Maps API
Used by apps like Uber or Zomato to display maps and live tracking.
Google Maps Platform offers documentation for developers.
PayPal Payment Understanding API
Enables secure payment processing on e-commerce sites.
Learn more at PayPal Developer Docs.
Twitter API
Helps apps fetch tweets, analyze hashtags, or add Twitter login.
Check Twitter API Overview.
Weather API basics
Provides real-time weather data for travel and fitness apps.
Example: OpenWeatherMap API.
YouTube Data API basics
Allows developers to integrate YouTube videos and analytics into their apps.
More details at YouTube API Docs.
(Explore our Beginner’s Guide to Web Development Tools for related resources.)
Benefits of Learning APIs for Beginners
- Builds understanding of modern app development and integrations.
- Enables creation of feature-rich projects using third-party services.
- Improves career prospects, as API knowledge is vital in software roles.
- Opens opportunities in cloud computing, IoT, and AI development.
Common API Use Cases
- Social logins (Login with Google/Facebook)
- Payment gateways (Stripe, PayPal)
- Maps and navigation (Google Maps API)
- Weather and news feeds (OpenWeatherMap, News API)
- Music and media streaming (Spotify API, YouTube API)
API vs Web Service
While many APIs are web-based, not all APIs are web services. APIs are broader and can include local library APIs, hardware APIs, or operating system APIs. Web services, on the other hand, specifically use internet protocols for communication.
(See GeeksforGeeks API vs Web Service for more details.)
FAQs
1. What does API stand for?
API stands for Application Programming Interface.
2. Do I need coding skills to use APIs?
Not always. Tools like Postman allow testing APIs without heavy coding.
3. Are APIs free to use?
Some are free (e.g., OpenWeatherMap API), others are paid or freemium (e.g., Google Maps API).
4. Why are APIs important for mobile apps?
They allow mobile apps to access external services like maps, authentication, or payments.
Conclusion
Understanding API introduction is vital for beginners entering software development. APIs connect apps, enabling smooth integrations like maps, payments, and logins. Learning how APIs work can help you build smarter, more connected applications — and open doors to careers in web, mobile, and cloud development.
(Want to learn APIs in-depth? Visit Chatrashala Tech Tutorials or explore Coursera API Development Courses.)