Top 10 Final Year Projects Ideas for Computer Science Students
August 4, 2025
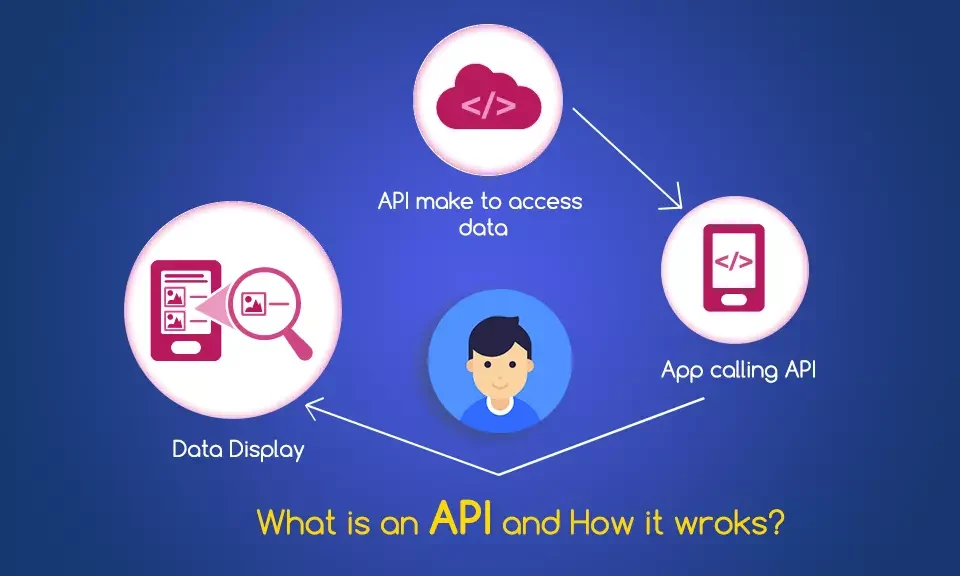
What is an API? Real-World Examples for Beginners
August 5, 2025Databases play a vital role in modern technology, powering everything from small desktop applications to large-scale enterprise systems. Two commonly discussed database systems are DBMS (Database Management System) and RDBMS (Relational Database Management System). Many students and beginners often confuse these terms, but understanding the DBMS vs. RDBMS differences is essential to choose the right approach for managing data effectively. In this guide, we will explain both systems in detail, highlight their key differences, and provide insights into their advantages and use cases.
(For additional learning, explore GeeksforGeeks DBMS Tutorial or W3Schools SQL Guide.)
What is DBMS?
A Database Management System (DBMS) is software that helps in storing, organizing, and managing data without manually handling raw files. It provides users with a way to perform essential operations like creating, reading, updating, and deleting data. DBMS is usually employed in small-scale applications where complex relationships between data are not required.
DBMS stores data in file systems and follows hierarchical or navigational structures. It allows developers to work with data more conveniently but does not inherently support relationships between different datasets. A good example of DBMS software is Microsoft Access, which is widely used in small business applications. Similarly, dBASE and Oracle Berkeley DB are also popular DBMS tools.
(For basics of DBMS, refer to TutorialsPoint DBMS Overview.)
What is RDBMS?
A Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) is an advanced form of DBMS that organizes data in a tabular format, meaning rows and columns. It introduces the concept of relationships between data through primary keys and foreign keys, allowing efficient handling of large datasets.
RDBMS is widely used in industries where data integrity and security are crucial. It supports SQL (Structured Query Language) as its standard language for querying and managing databases. Popular RDBMS examples include MySQL, Oracle Database, PostgreSQL, and Microsoft SQL Server, all of which are extensively used in enterprise applications and web development.
(To learn more about RDBMS, check Oracle Database Documentation.)
Understanding DBMS vs. RDBMS Differences
When comparing DBMS vs. RDBMS differences, the first noticeable distinction is in how data is stored and managed. DBMS relies on file-based storage systems that organize data in a hierarchical or navigational structure, while RDBMS uses a relational model where data is organized into tables and linked through keys. This relational approach allows RDBMS to efficiently manage complex data structures and relationships, making it ideal for large-scale applications like banking systems or e-commerce platforms.
Another significant difference lies in data integrity. RDBMS ensures data consistency by enforcing constraints like primary keys, foreign keys, and unique keys. This means that duplicate or invalid data cannot easily enter the system. On the other hand, DBMS often relies on application-level checks to maintain integrity, which can be prone to errors.
Security is also a major factor. RDBMS provides advanced user authentication and role-based permissions, making it suitable for applications where sensitive data, such as financial or healthcare information, must be protected. DBMS, by contrast, offers more basic access control and is suitable for smaller applications where security is less of a concern.
Scalability is another crucial factor. RDBMS can handle massive amounts of data and support multiple users concurrently without performance degradation. DBMS systems are generally lightweight and designed for single-user or small-team environments.
(For a detailed breakdown, visit Javatpoint’s guide on DBMS vs RDBMS.)
Advantages of RDBMS Over DBMS
One of the main advantages of RDBMS is data integrity. By enforcing relationships and constraints, RDBMS ensures data remains accurate and consistent across the system. This is particularly important in large organizations where data accuracy directly affects business decisions.
Another advantage is enhanced security. RDBMS systems come with built-in authentication, encryption, and role-based access controls, making them far more secure than traditional DBMS solutions.
Support for SQL is also a significant benefit. SQL provides a powerful and standardized way to query and manipulate data, which DBMS lacks. This makes RDBMS far more versatile for developers and data analysts working on complex applications.
Lastly, scalability and multi-user support make RDBMS the go-to choice for enterprise-level projects. It can manage large databases efficiently, ensuring smooth performance even under heavy loads.
When Should You Choose DBMS vs. RDBMS?
The decision to use DBMS or RDBMS depends on the scale and complexity of your project. For small-scale applications, such as personal data tracking, offline inventory systems, or prototypes, DBMS is sufficient because it is lightweight and easy to implement.
However, if your application involves large datasets, multiple users, or requires strict data integrity (like banking systems, online retail, or enterprise-level ERP software), RDBMS is the superior choice. Its relational structure and robust features make it a standard in modern database management.
(Beginner-friendly explanation available at IBM’s DBMS Concepts.)
Real-Life Examples of DBMS and RDBMS
Microsoft Access is a classic example of DBMS. It is used by small businesses for managing customer data or tracking inventory, as it is simple to set up and doesn’t require advanced features.
In contrast, MySQL and PostgreSQL are examples of RDBMS that power popular web applications such as WordPress websites, e-commerce platforms, and social media systems. Companies like Facebook and YouTube rely on RDBMS to handle vast amounts of data across millions of users while maintaining speed and accuracy.
Advantages and Disadvantages of DBMS
DBMS is lightweight and easy to install, making it perfect for personal use or single-user applications. It requires fewer resources and is often less expensive. However, it lacks advanced features like relationship management, multi-user capabilities, and robust security, limiting its use in large or sensitive applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of RDBMS
RDBMS excels at handling large datasets and complex relationships. It supports SQL, enforces data integrity, and provides excellent security. On the downside, RDBMS can be resource-intensive, requiring more memory and processing power, and may involve more complex setup and maintenance compared to basic DBMS solutions.
FAQs on DBMS vs. RDBMS Differences
What is the primary difference between DBMS and RDBMS?
The key difference lies in data organization. DBMS uses file systems, while RDBMS organizes data in relational tables and enforces relationships.
Which is more widely used today?
RDBMS is the standard in modern applications, powering everything from e-commerce sites to enterprise software.
Is SQL exclusive to RDBMS?
Yes, SQL is the standard language used by RDBMS to manage relational data, whereas DBMS systems may not use SQL at all.
Can DBMS handle large-scale projects?
DBMS is typically unsuitable for large-scale applications due to its limited scalability and lack of relational features.
Conclusion
Understanding the DBMS vs. RDBMS differences is essential for students, developers, and IT professionals. While DBMS is useful for smaller, simpler applications, RDBMS dominates modern software development due to its relational model, robust security, and scalability. Choosing the right system depends on your project’s scale, data complexity, and security needs.